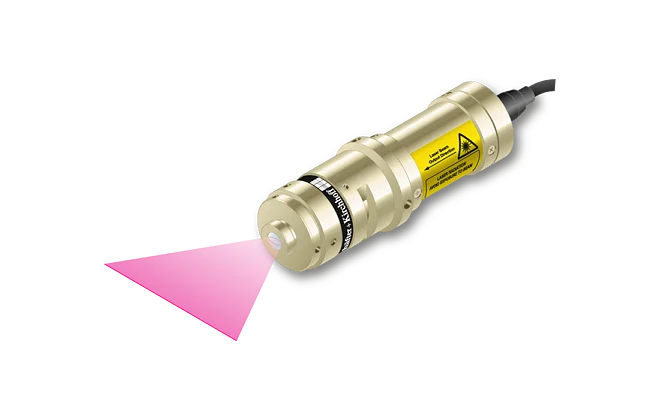
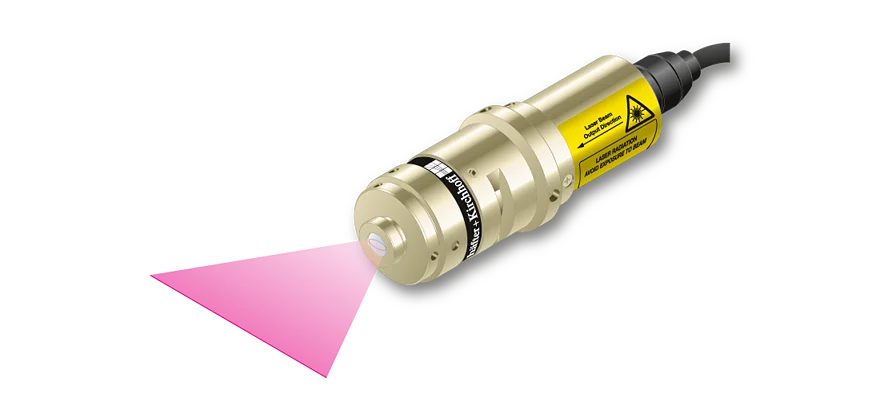
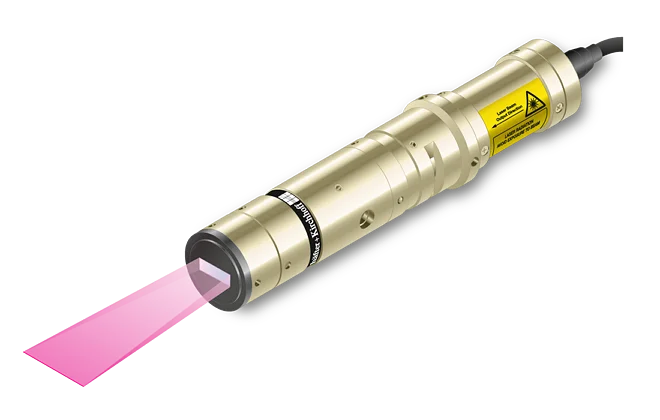
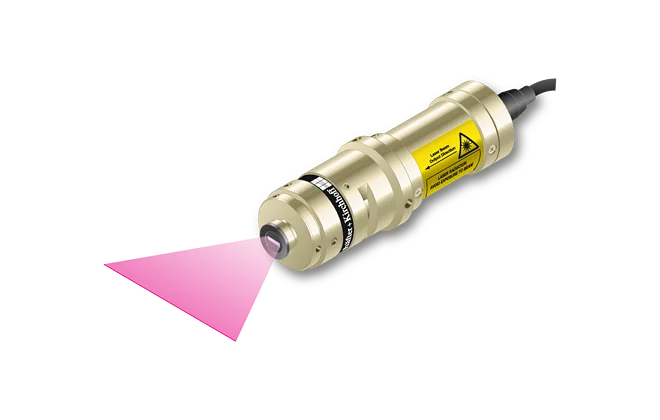
Features
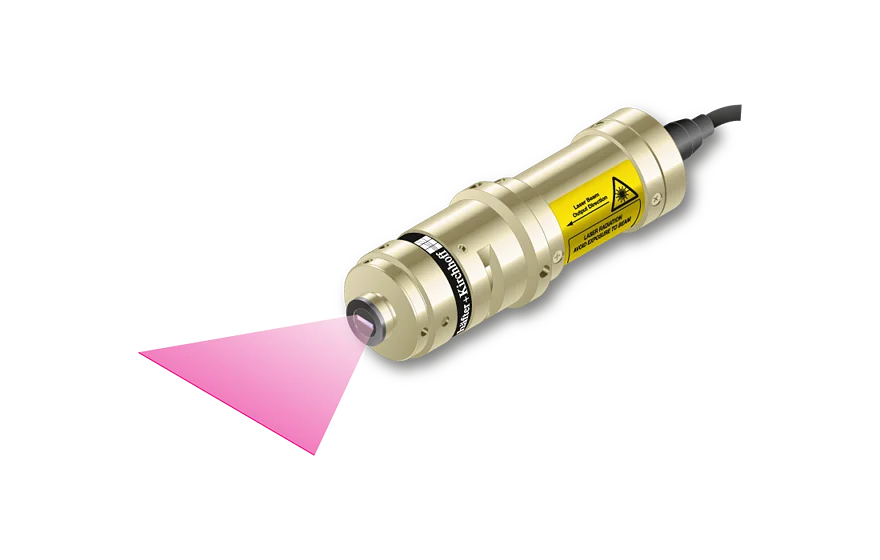
- Depth of focus 7 to 35 times larger than for corresponding Micro Focus Generator
- Line widths starting at 84 µm
- Wavelengths 405 - 940 nm
- Laser powers up to 30 mW
- Low noise Laser Module (typ. < 0.15 % of Po (RMS, Bandwidth < 1 MHz))
- Discontinued